

If two soap bubbles of different radii are connected by a tube…?.Bernoulli’s principle is based on the law of conservation of…?.
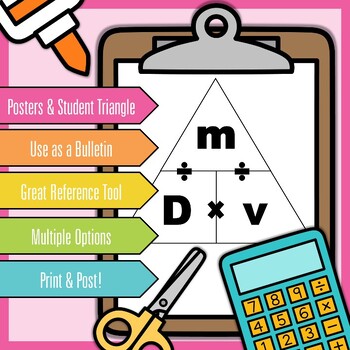
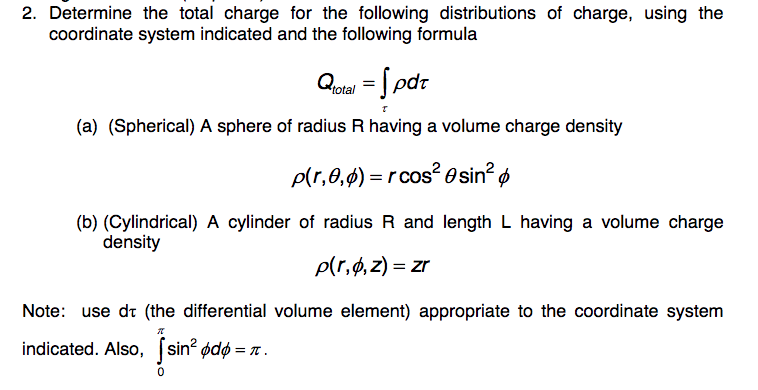
If the work done in blowing a bubble of volume V is W, then the work done in…?.Consider a soap film on a rectangular frame of wire of area 4×4cm 2.A uniform capillary tube of inner radius r is dipped vertically into a beaker filled with water…?.If the excess pressure inside a soap bubble is balanced by an oil column of height…?.A solid sphere falls with a terminal velocity of 20m/s in air.Life tubes and ships are two applications of the concept of density.The density is classified into two types namely, absolute density and relative density.The CGS unit of density is gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm3).1 gram/cubic centimeter, is commonly used as the standard value for calculating the density of different substances. Solids are denser than liquids and liquids are denser than gases.The density of an object can be calculated by the formula: ρ = m/v.Density is defined as the measurement of the mass of an object or body with a unit volume.When this reduced density is combined with the buoyant force it allows the ship to float over water. These tanks offer large volumes with little mass which thereby decreases the ship’s density. Ships: Ships can float in water because they are designed with ballast tanks for holding air.Life tubes float because they are filled with air which is less dense than water.

 Life Tubes: The life tubes are found in swimming pools or beaches and are designed in such a way that they float in water and protect people from drowning while swimming. As a result, the balloon filled with air is light and the balloon filled with coke is heavy. On the other hand, in an air balloon, the atoms collide with each other very quickly and therefore take up more space or less density. Coke is much denser because its atoms move around less and take up less space. Consider two balloons, one is filled with air while the other is filled with coke. The real-life applications of density include: It is defined as the ratio of the material’s density to the reference material’s density. Relative Density: The relative density is also known as specific gravity. Absolute Density: The mass of any substance per unit volume of a material is defined as absolute density. The density is classified into two types as follows: Let us look at the densities of some substances: Aluminium, glass, and bamboo are some examples of sparse materials which are the opposite of dense materials. Materials with high density are harder and they are more “likely” to feel heavy. Lead, iron, and platinum are various examples of dense materials. To understand the concept of density better, let us look at a couple of examples: The liquids are less dense than solids because the particles are not tightly packed in liquid but denser than gases which contain free-flowing particles. The particles in solids are tightly packed with very little space between them, therefore the solids are denser than liquids and gases. The density of an object can be calculated by the formula: Megagram (metric ton) per cubic meter (mg/m 3)įurthermore, the CGS unit of density is gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm 3). Gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm 3) - 1 g/cm 3 = 1000 kg/m 3. The other units of density are as follows: If we talk about other density units, metric tons and liter are also used despite the fact that they are not part of the SI unit system. The density of different substances is different which means that the different substances with similar volumes will weigh differently. In a qualitative term, it indicates how heavy an object can be at constant volume. Density is measured with the SI unit as Kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m 3).Įven though the SI unit of density is kg/m³, the other commonly used units to measure density are:ĭensity is defined as the relationship between the substance’s mass and the volume it occupies.
Life Tubes: The life tubes are found in swimming pools or beaches and are designed in such a way that they float in water and protect people from drowning while swimming. As a result, the balloon filled with air is light and the balloon filled with coke is heavy. On the other hand, in an air balloon, the atoms collide with each other very quickly and therefore take up more space or less density. Coke is much denser because its atoms move around less and take up less space. Consider two balloons, one is filled with air while the other is filled with coke. The real-life applications of density include: It is defined as the ratio of the material’s density to the reference material’s density. Relative Density: The relative density is also known as specific gravity. Absolute Density: The mass of any substance per unit volume of a material is defined as absolute density. The density is classified into two types as follows: Let us look at the densities of some substances: Aluminium, glass, and bamboo are some examples of sparse materials which are the opposite of dense materials. Materials with high density are harder and they are more “likely” to feel heavy. Lead, iron, and platinum are various examples of dense materials. To understand the concept of density better, let us look at a couple of examples: The liquids are less dense than solids because the particles are not tightly packed in liquid but denser than gases which contain free-flowing particles. The particles in solids are tightly packed with very little space between them, therefore the solids are denser than liquids and gases. The density of an object can be calculated by the formula: Megagram (metric ton) per cubic meter (mg/m 3)įurthermore, the CGS unit of density is gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm 3). Gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm 3) - 1 g/cm 3 = 1000 kg/m 3. The other units of density are as follows: If we talk about other density units, metric tons and liter are also used despite the fact that they are not part of the SI unit system. The density of different substances is different which means that the different substances with similar volumes will weigh differently. In a qualitative term, it indicates how heavy an object can be at constant volume. Density is measured with the SI unit as Kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m 3).Įven though the SI unit of density is kg/m³, the other commonly used units to measure density are:ĭensity is defined as the relationship between the substance’s mass and the volume it occupies.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
